Products 101
Return to Agent Welcome Page
Here’s a detailed comparison of the Top 10 key financial accounts,
covering rules, limits, taxation, age restrictions, and other important details:
Comparison Table
Account | Tax Treatment | Contribution Limits (2024) | Age Restrictions | Early Withdrawal Penalty | RMDs? |
| Traditional IRA | Tax-deferred, taxed at withdrawal | 7K(7K(8K 50+) | No (earned income) | 10% before 59½ | Yes (73) |
| Roth IRA | Tax-free growth | 7K(7K(8K 50+) | Income limits apply | Earnings penalized | No |
| MMA | Taxed annually | None | None | None (limited withdrawals) | No |
| CD | Taxed annually | None | None | Early surrender penalty | No |
| Stocks | Capital gains/dividends | None | None | None (but capital gains tax) | No |
| IUL | Tax-deferred, tax-free loans | Flexible | None | Surrender charges | No |
| Whole Life | Tax-deferred, tax-free loans | Premium-based | None | Surrender charges | No |
| FIA | Tax-deferred | None (min. premium) | None | Surrender penalty + 10% IRS | No |
| 401(k) | Traditional: Tax-deferred; Roth: Tax-free | 23K(23K(30.5K 50+) | No (employed) | 10% before 59½ | Yes (73) |
| TSP | Traditional/Roth like 401(k) | 23K(23K(30.5K 50+) | No (employed) | 10% before 59½ | Yes (73) |
Key Takeaways
- Tax-Advantaged Retirement Accounts (IRA, 401(k), TSP): Best for long-term savings with tax benefits, restrictions to age.
- Roth vs. Traditional: Roth offers tax-free withdrawals; Traditional offers upfront deductions.
- Insurance Products (IUL, Whole Life, FIA): Provide tax-deferred growth but are more complex and offer a Death Benefit.
- Safe Savings (MMA, CD): Low risk, FDIC-insured, but lower returns.
- Stocks: Highest growth potential but volatile.
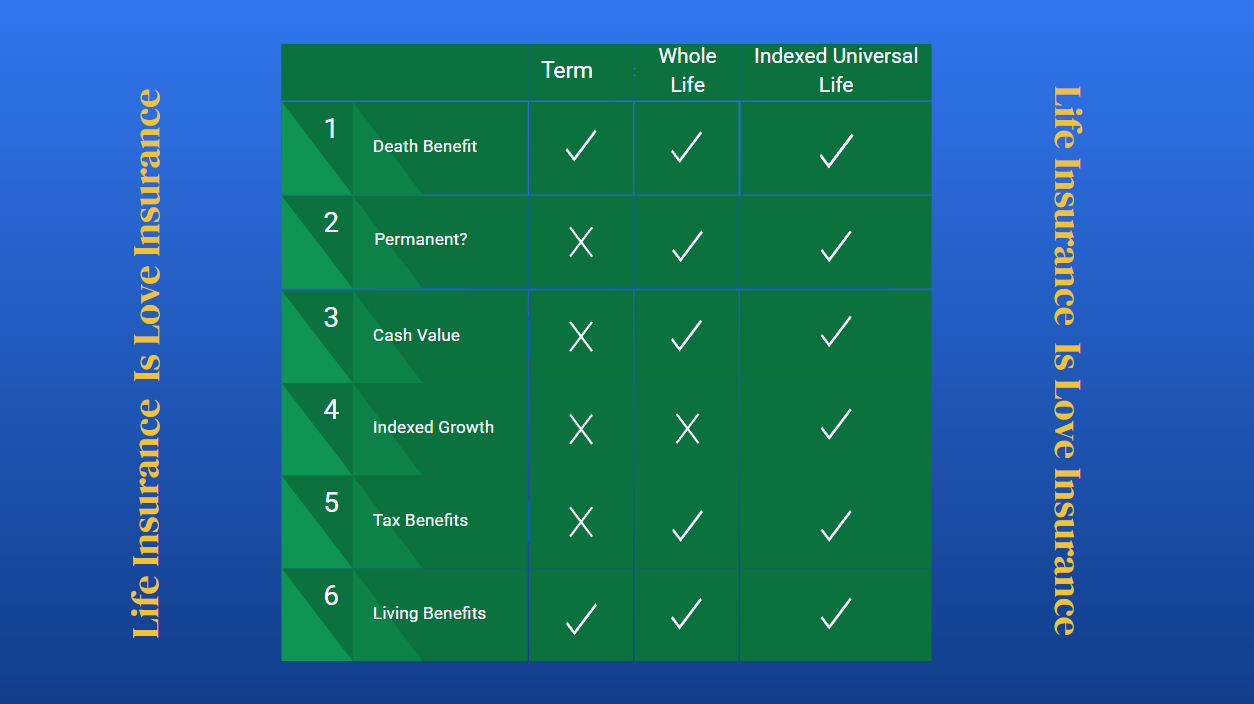
3 Types of Life Insurance Compared
 Referral Network
Referral Network